DML
INSERT
insert_stmt:
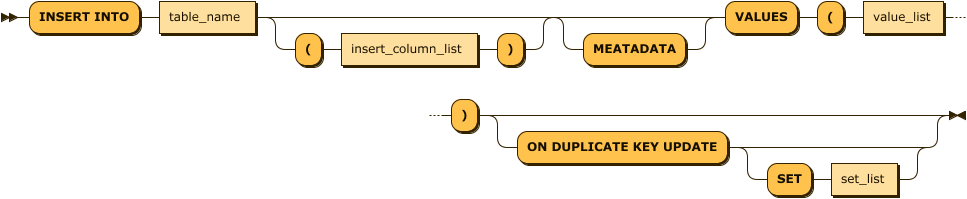
insert_column_list:
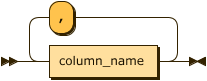
value_list:
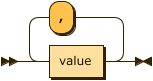
set_list:
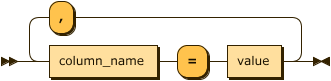
insert_stmt ::= 'INSERT INTO' table_name ( '(' insert_column_list ')' )? 'METADATA'? 'VALUES' '(' value_list ')' ( 'ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE' ( 'SET' set_list )? )?
insert_column_list ::= column_name ( ',' column_name )*
value_list ::= value ( ',' value )*
set_list ::= column_name '=' value ( ',' column_name '=' value )*create table test (number int,name varchar(20));
Created successfully.
insert into test values (1,"test");
1 row(s) inserted.
insert into test(name,number) values ("test",2);
1 row(s) inserted.This is the syntax for entering values into a specific table. One unusual thing is that columns not specified in Column_List are all filled with NULL values. This is a policy considering the characteristics of log files adopted for convenience of input and efficiency of storage space. METADATA is only available for tag tables.
INSERT ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE
Machbase supports syntax similar to the commonly known UPSERT function.
A special syntax that can be used when entering a value into a Lookup/Volatile table with a primary key specified. If the table already contains data with a duplicate primary key value, the value of the existing data is changed. Of course, when there is no duplicated key value data, it is inserted as new data.
To use this syntax, the primary key must be specified in the volatile table.
If the column value of the inserted data is different from the column value of the updated data, or if it is desired to update a column value other than the column value of the inserted data, the SET clause can be further input.
- The SET clause consists of ‘column = value’, each separated by a comma.
- You must not change the default key value in the SET clause.
INSERT SELECT
insert_select_stmt:
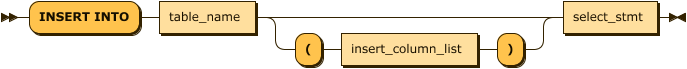
insert_select_stmt ::= 'INSERT INTO' table_name ( '(' insert_column_list ')' )? select_stmtThis statement inserts the result of the SELECT statement on a specific table. In basic, it is similar to other DBMSs, but with the following differences.
- The _ARRIVAL_TIME column value is entered as the time value at the time the INSERT SELECT statement is executed unless specified in the select and INSERT column lists.
- If the input value to be inserted for a VARCHAR type column is greater than the maximum length of the column, the maximum length of the corresponding column is entered without error.
- If type conversion is possible (numeric -> numeric), it is inserted according to the input column value.
- ROLLBACK does not occur if an error occurs during execution.
- If you insert a value in the _ARRIVAL_TIME column, the new value will not be entered if it has a time before the existing value.
create table t1 (i1 integer, i2 varchar(60), i3 varchar(5));
Created successfully.
insert into t1 values (1, 'a', 'ddd' );
1 row(s) inserted.
insert into t1 values (2, 'kkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkk', 'c');
1 row(s) inserted.
insert into t1 select * from t1;
2 row(s) inserted.
create table t2 (i1 integer, i2 varchar(60), i3 varchar(5));
insert into t2 (_arrival_time, i1, i2, i3) select _arrival_time, * from t1;
4 row(s) inserted.UPDATE
- This function is available from 5.5.
update_stmt:

update_expr_list:

update_expr:

update_stmt ::= 'UPDATE' table_name ( 'METADATA' )? 'SET' update_expr_list 'WHERE' primary_key_column '=' value
update_expr_list ::= update_expr ( ',' update_expr)*
update_expr ::= column '=' valueINSERT ON DUPLICATE UPDATE syntax is also provided, rather than UPSERT via a KEY UPDATE. You can also use the Primary Key to enter values into the specified Lookup/Volatile table. In the WHERE clause, you must create a matching predicate for the primary key.
UPDATE METADATA
Only for the TAGDATA table, when you want to update the metadata.
UPDATE TAG METADATA SET ...- The metadata of the TAGDATA table can not be entered/modified through INSERT ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE.
DELETE
delete_stmt:
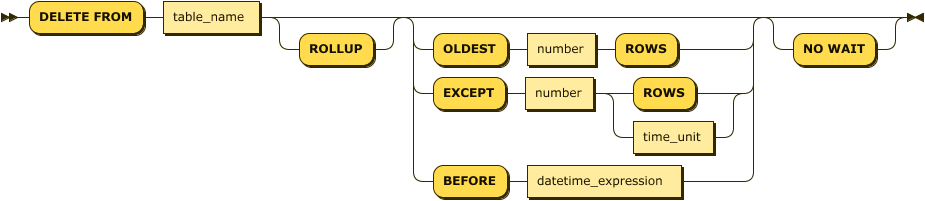
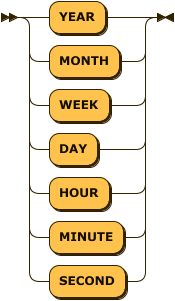
time_unit:
delete_stmt ::= 'DELETE FROM' table_name ( 'OLDEST' number 'ROWS' | 'EXCEPT' number ( 'ROWS' | time_unit ) | 'BEFORE' datetime_expression )? 'NO WAIT'?
time_unit ::= 'DURATION' number time_unit ( ( 'BEFORE' | 'AFTER' ) number time_unit )?The DELETE statement in Machbase can be performed on the log table. In addition, it is not possible to delete data in an arbitrary position in the middle, and it is possible to erase consecutively from the arbitrary position to the last (oldest log) record.
This is a policy that takes advantage of the characteristics of log data. It is a DB format representation of the act of deleting a file in order to secure space when it is entered once.
The syntax of DURATION, OLDEST, and EXCEPT cannot be used for TAG and Rollup tables.
-- Delete all.
DELETE FROM devices;
-- Delete oldest last N rows.
DELETE FROM devices OLDEST N ROWS;
-- Delete all except recent N rows.
DELETE FROM devices EXCEPT N ROWS;
-- Delete all except N matches from now on.
DELETE FROM devices EXCEPT N DAY;
-- Delete all data from before June 1, 2014.
DELETE FROM devices BEFORE TO_DATE('2014-06-01', 'YYYY-MM-DD');
-- Delete tag data from before June 1, 2014.
DELETE FROM tag BEFORE TO_DATE('2014-06-01', 'YYYY-MM-DD');
-- Delete tag rollup data from before June 1, 2014.
DELETE FROM tag ROLLUP BEFORE TO_DATE('2014-06-01', 'YYYY-MM-DD');DELETE WHERE
delete_where_stmt:

delete_where_stmt ::= 'DELETE FROM' table_name 'WHERE' column_name '=' valuecreate volatile table t1 (i1 int primary key, i2 int);
Created successfully.
insert into t1 values (2,2);
1 row(s) inserted.
delete from t1 where i1 = 2;
1 row(s) deleted.- You can only delete records that match the conditions created in the WHERE clause, which can only be performed on volatile tables.
- The primary key can only be performed on the specified volatile table.
- The WHERE clause allows only conditions of (primary key column) = (value), and can not be created with other conditions.
- You can not use a column other than the primary key column in the condition.
delete_from_tag_where_stmt:
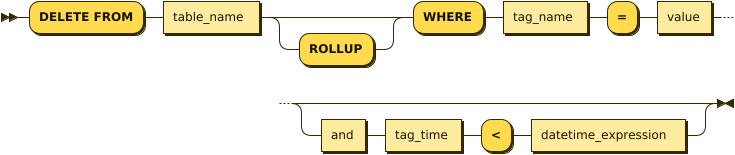
delete_from_tag_where_stmt ::= 'DELETE FROM' table_name 'ROLLUP'? 'WHERE' tag_name '=' value ( and tag_time '<' datetime_expression )?A Tag or Rollup table supports the following two types of DELETE statements.
- Delete by tag name
- Delete by tag name and tag time
-- Delete by tag name
DELETE FROM tag WHERE tag_name = 'my_tag_2021'
-- Delete by tag name and tag time
DELETE FROM tag WHERE tag_name = 'my_tag_2021' AND tag_time < TO_DATE('2021-07-01', 'YYYY-MM-DD');
-- Delete rollup by tag name
DELETE FROM tag ROLLUP WHERE tag_name = 'my_tag_2021'
-- Delete rollup by tag name and tag time
DELETE FROM tag ROLLUP WHERE tag_name = 'my_tag_2021' AND tag_time < TO_DATE('2021-07-01', 'YYYY-MM-DD');- The time it takes for the deleted row to be physically deleted from the storage space after the deletion query is executed may vary depending on the situation of the DBMS.
LOAD DATA INFILE
load_data_infile_stmt:
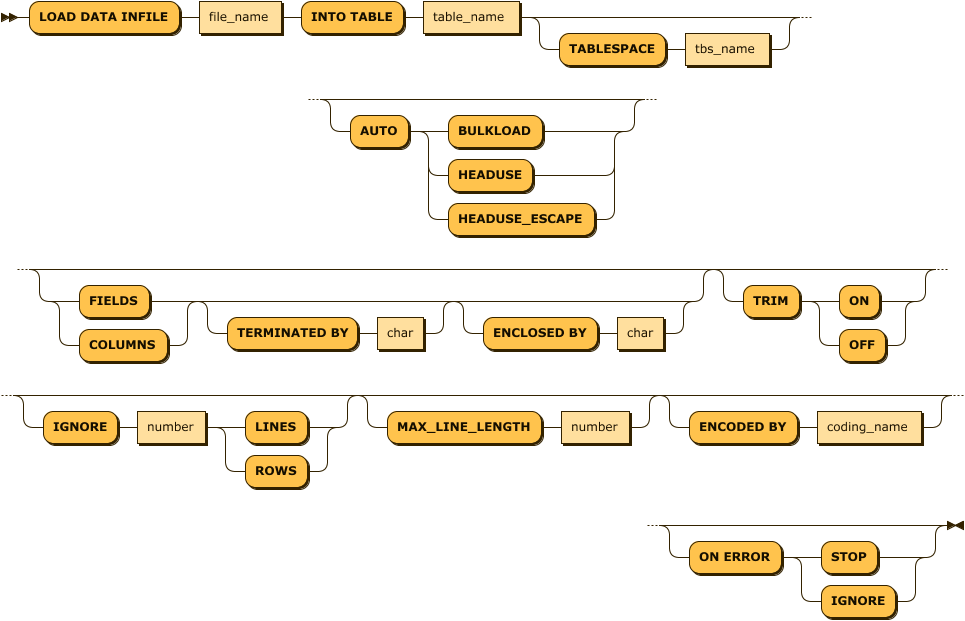
load_data_infile_stmt: 'LOAD DATA INFILE' file_name 'INTO TABLE' table_name ( 'TABLESPACE' tbs_name )? ( 'AUTO' ( 'BULKLOAD' | 'HEADUSE' | 'HEADUSE_ESCAPE' ) )? ( ( 'FIELDS' | 'COLUMNS' ) ( 'TERMINATED BY' char )? ( 'ENCLOSED BY' char )? )? ( 'TRIM' ( 'ON' | 'OFF' ) )? ( 'IGNORE' number ( 'LINES' | 'ROWS' ) )? ( 'MAX_LINE_LENGTH' number )? ( 'ENCODED BY' coding_name )? ( 'ON ERROR' ( 'STOP' | 'IGNORE' ) )?CSV format data files are read directly from the server, and tables and columns are created directly from the server according to the options and input them. Each option is explained as follows
| Options | Description |
|---|---|
| AUTO mode_string mode_string = (BULKLOAD | HEADUSE | HEADUSE_ESCAPE) | Creates the corresponding table and automatically generates the column type (varchar type for automatic creation) and the column name. BULKLOAD: Enters one row of data as one column. It is used for data that can not be divided into columns. HEADUSE: Uses the column name as described in the first line of the data file as the column name of the table, and creates as many columns as there are in the line. HEADUSE_ESCAPE: Similar to the HEADUSE option, but appends a ‘’ character to the front and back of the column name to avoid errors that can occur if the column name is the same as the reserved word in the DB. If a special character exists in the column name, changes it to ‘’. |
(FIELDS|COLUMNS) TERMINATED BY ’term_char’ ESCAPED BY ’escape_char’ | Specifies the delimiter (term_char) and escape character (escape_char) for parsing the data line. For common CSV files, the delimiter is , and the escape character is ‘. |
| ENCODED BY coding_name coding_name = { UTF8(default) | MS949 | KSC5601 | EUCJP | SHIFTJIS | BIG5 | GB231280 } | Specifies the encoding options for the data file. The default value is UTF-8. |
| TRIM (ON | OFF) | Removes or maintains the empty space of the column. The default is ON. |
| IGNORE number (LINES | ROWS) | Ignores data for a specified number of lines or lines. It is used to ignore header of CSV format file or ignore VCF header. |
| MAX_LINE_LENGTH | Specifies the maximum length of one line. The default value is 512K. If the data is larger, you can specify a larger value. |
| ON ERROR (STOP | IGNORE) | Specifies the action to take when an error occurs during input. If it is STOP, input is stopped. If it is IGNORE, the line where error occurred is skipped and input is continued. The default is IGNORE. |
-- Use default field delimiter(,) field encloser (") to input data.
LOAD DATA INFILE '/tmp/aaa.csv' INTO TABLE Sample_data ;
-- Create NEWTABLE with one column and enter one line as one column.
LOAD DATA INFILE '/tmp/bbb.csv' INTO TABLE NEWTABLE AUTO BULKLOAD;
-- Create NEWTABLE using first line of csv as column information, and input it into table.
LOAD DATA INFILE '/tmp/bbb.csv' INTO TABLE NEWTABLE AUTO HEADUSE;
-- First line is ignored and field delimiter is ; and enclosing character is specified by '.
LOAD DATA INFILE '/tmp/ccc.csv' INTO TABLE Sample_data FIELDS TERMINATED BY ';' ENCLOSED '\'' IGNORE 1 LINES ON ERROR IGNORE;- If the AUTO option is not used, all columns of the table must be created as VARCHAR or TEXT types.