파형 데이터 만들기
이 튜토리얼은 순수 셸 스크립트만으로 데이터베이스에 데이터를 쓰고 읽는 방법을 설명합니다.
CREATE TAG TABLE IF NOT EXISTS EXAMPLE (
NAME VARCHAR(20) PRIMARY KEY,
TIME DATETIME BASETIME,
VALUE DOUBLE SUMMARIZED
);데이터 쓰기
machbase-neo에 데이터를 쓰는 가장 간단한 방법은 명령줄 도구 machbase-neo shell을 사용하는 것입니다.
이 도구를 이용해 테이블을 가져오고(import), 내보내고(export), 조회할 수 있습니다.
데이터 생성
예시에서는 1초마다 사인/코사인값을 출력하는 간단한 셸 스크립트를 사용합니다.
아래 스크립트를 복사해 gen_wave.sh로 저장하십시오.
#!/bin/bash
angle=0
step_angle=24
sinval=0
cosval=0
PI=3.14159
while [ 1 ]
do
ts=`date +"%s"`
sinval=$(awk "BEGIN{ printf \"%.6f\", (sin($angle*($PI/180)))}")
cosval=$(awk "BEGIN{ printf \"%.6f\", (cos($angle*($PI/180)))}")
echo "wave.sin,$ts,$sinval"
echo "wave.cos,$ts,$cosval"
sleep 1
angle=$((angle+step_angle))
done스크립트 실행
작성한 스크립트를 실행해 봅니다.
sh ./gen_wave.sh스크립트는 매초 wave.sin, wave.cos 이름과 함께 유닉스 타임스탬프, 값을 CSV 형식으로 출력합니다.
이 출력은 machbase-neo shell에서 바로 사용할 수 있습니다.
종료하려면 Ctrl+C를 누르십시오.

출력 CSV의 컬럼 순서는 테이블 구조에 맞춰야 합니다.
테이블 구조는 다음 명령으로 확인할 수 있습니다.
machbase-neo shell desc EXAMPLEdesc <table> 서브커맨드는 테이블 정보를 보여 줍니다.
TABLE EXAMPLE
TYPE Tag Table
TAGS wave.cos, wave.sin
┌───┬───────┬──────────┬────────┐
│ # │ NAME │ TYPE │ LENGTH │
├───┼───────┼──────────┼────────┤
│ 1 │ NAME │ varchar │ 100 │
│ 2 │ TIME │ datetime │ 8 │
│ 3 │ VALUE │ double │ 8 │
└───┴───────┴──────────┴────────┘CSV를 테이블에 가져올 때는 컬럼 순서와 데이터 타입을 반드시 테이블 정의와 일치시켜야 합니다.
스크립트와 명령어 결합
이제 스크립트 출력을 machbase-neo shell 입력으로 사용할 수 있습니다.
sh gen_wave.sh | machbase-neo shell import --timeformat=s EXAMPLEmachbase-neo는 모든 타임스탬프를 나노초 단위로 다룹니다. 하지만 셸 스크립트는
date 명령으로 초 단위 타임스탬프를 생성하므로
--timeformat 옵션으로 CSV 데이터의 시간이 초 단위임을 명시해야 합니다.자세한 내용은
machbase-neo shell help timeformat을 참고해 주세요.A each line of CSV that are generated by shell script is processed in machbase-neo shell import then “import” into EXAMPLE table.
동일한 방식으로 직접 데이터를 입력할 수도 있습니다.
echo "wave.pi,1674860125,3.141592" | machbase-neo shell import -t s EXAMPLEor
echo "wave.pi,`date +%s`,3.141592" | machbase-neo shell import -t s EXAMPLE이제 최신 값을 조회해 보겠습니다.
machbase-neo shell "select * from EXAMPLE where NAME='wave.pi' order by time desc limit 1"
데이터 읽기
SQL 쿼리
스크립트가 실행 중인 동안…
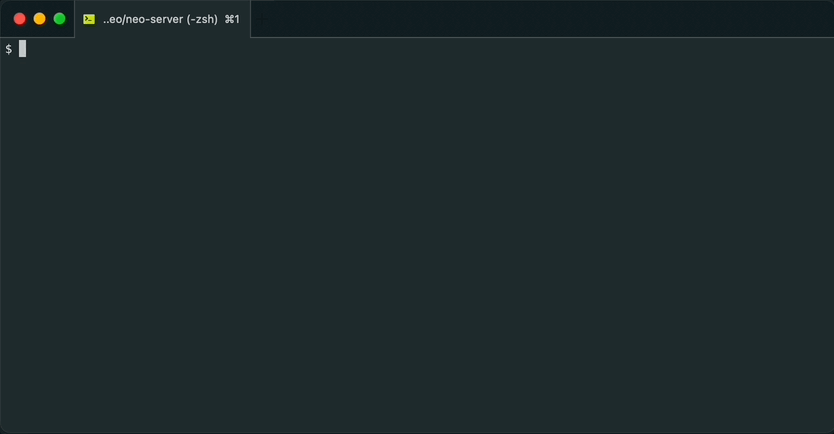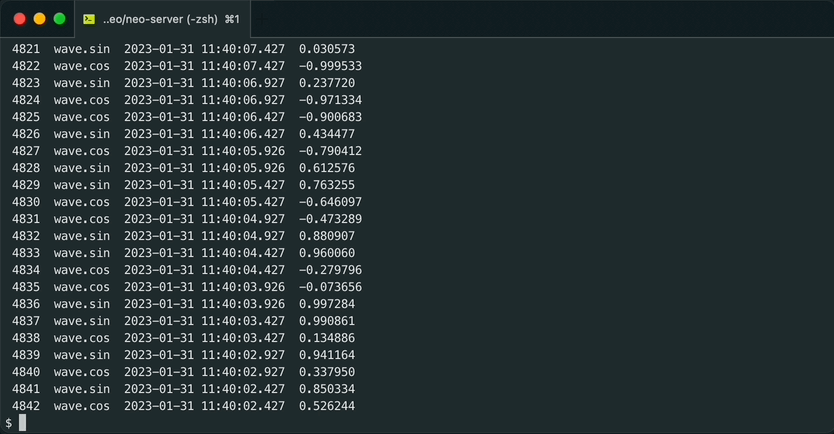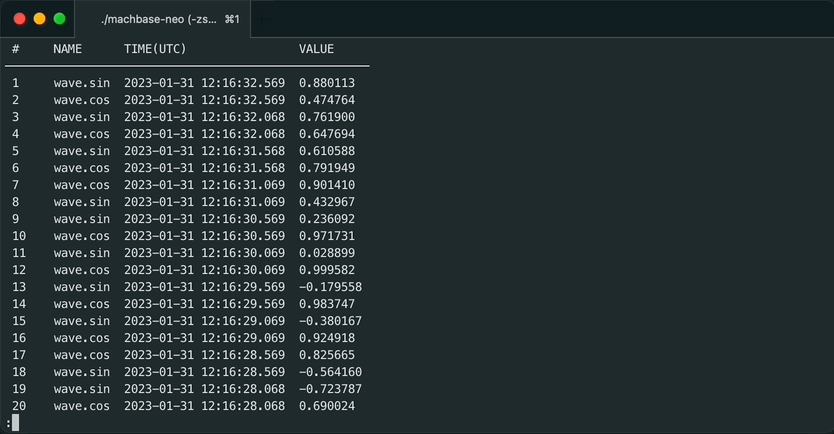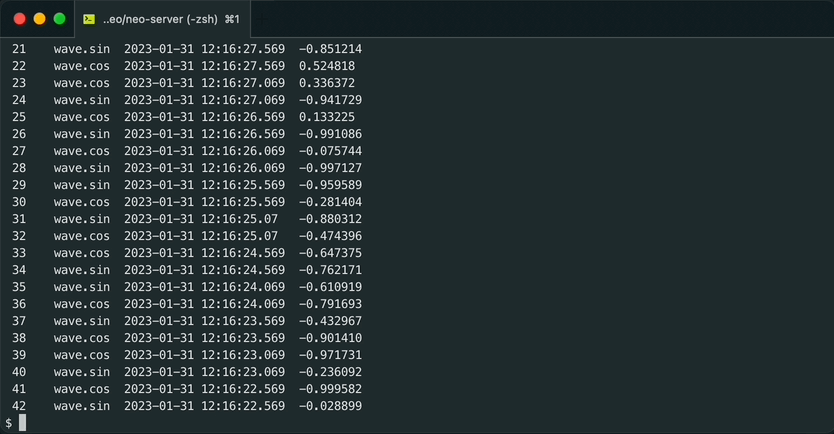
sh gen_wave.sh | machbase-neo shell import --timeformat=s EXAMPLESQL 쿼리로 데이터를 출력합니다.
machbase-neo shell "select * from EXAMPLE order by time desc" # NAME TIME(UTC) VALUE
────────────────────────────────────────────────
1 wave.sin 2023-01-28 14:03:59 0.214839
2 wave.cos 2023-01-28 14:03:59 -0.976649
3 wave.sin 2023-01-28 14:03:58 0.593504
4 wave.cos 2023-01-28 14:03:58 -0.804831
...
위 예제에서 machbase-neo shell 명령에 sql 서브커맨드를 명시하지 않았지만 쿼리가 정상 수행되었습니다.
이는 추가 인자나 옵션이 없을 경우 기본적으로 sql 서브커맨드를 사용하는 동작 때문입니다.
즉, machbase-neo shell "select..."는 machbase-neo shell sql "select..."와 같습니다.
옵션을 함께 사용할 때는 아래처럼 sql 서브커맨드를 명시해 주는 것이 좋습니다.
machbase-neo shell sql \
--tz America/Los_Angeles \
"select * from EXAMPLE order by time desc limit 4" # NAME TIME(AMERICA/LOS_ANGELES) VALUE
───────────────────────────────────────────────────
1 wave.sin 2023-01-28 06:03:59 0.214839
2 wave.cos 2023-01-28 06:03:59 -0.976649
3 wave.cos 2023-01-28 06:03:58 -0.804831
4 wave.sin 2023-01-28 06:03:58 0.593504machbase는 시간을 기본적으로 UTC로 표시합니다.
다른 시간대로 표시하려면 --tz 옵션을 사용하십시오.
local 또는 Europe/Paris와 같은 TZ 데이터베이스 문자열을 사용할 수 있습니다.
machbase-neo shell sql \
--tz local \
"select * from EXAMPLE order by time desc limit 4" # NAME TIME(LOCAL) VALUE
─────────────────────────────────────────────
1 wave.sin 2023-01-28 23:03:59 0.214839
2 wave.cos 2023-01-28 23:03:59 -0.976649
3 wave.cos 2023-01-28 23:03:58 -0.804831
4 wave.sin 2023-01-28 23:03:58 0.593504Table view
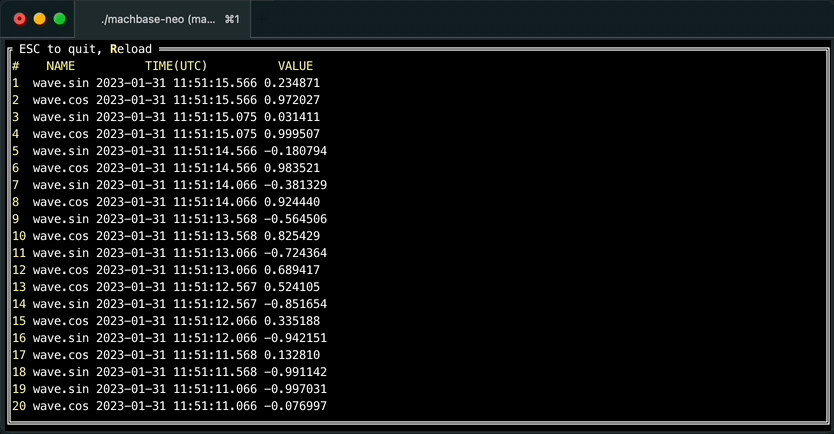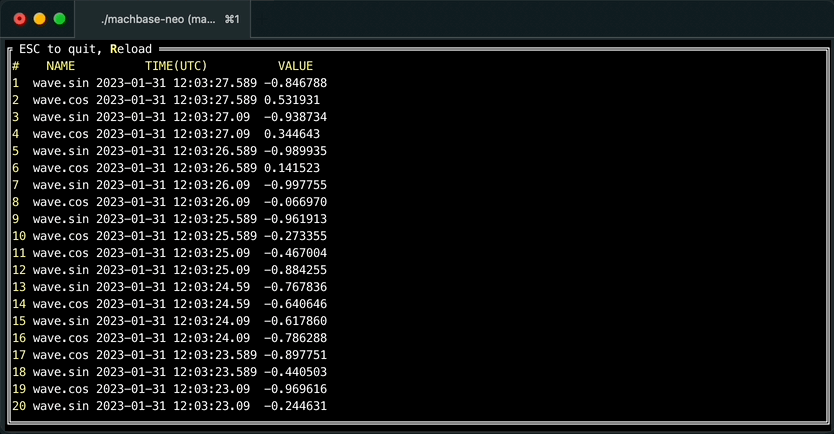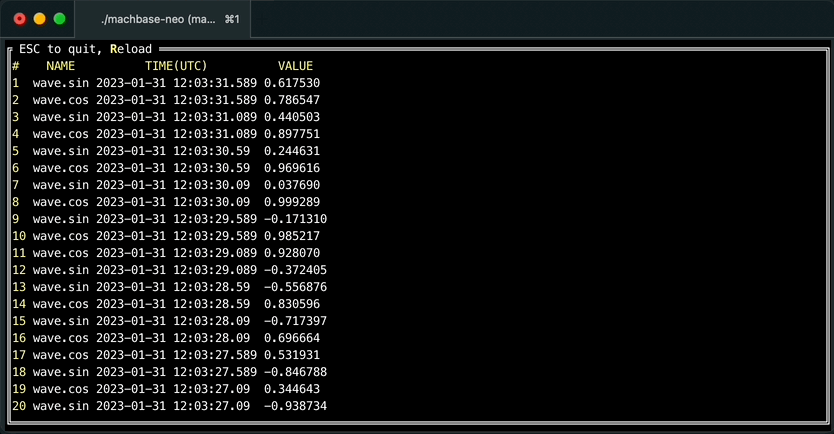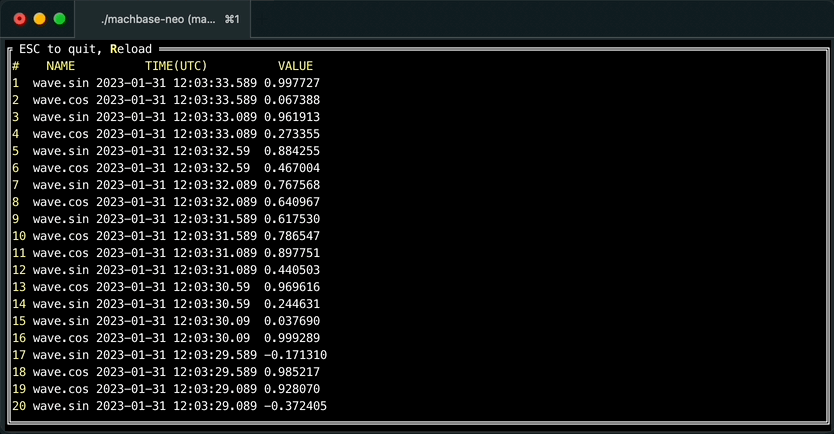
It is also possible browsing query result forward/backward with “walk” command like below.
machbase-neo shell walk "select * from EXAMPLE order by time desc"Then you can scroll up/down with keyboard, press ESC to exit table view.
Press r to re-execute query to refresh result, it is particularly useful with query was sorted by order by time desc to see the latest values when data is continuously being written.
Query Output format
JSON
Use --format json option
machbase-neo shell sql \
--format json \
"select * from EXAMPLE order by time desc limit 4"{
"data": {
"columns": ["ROWNUM","NAME","TIME(UTC)","VALUE"],
"types": ["string","string","datetime","double"],
"rows": [
[1,"wave.sin","2023-01-28 14:03:59",0.214839],
[2,"wave.cos","2023-01-28 14:03:59",-0.976649],
[3,"wave.cos","2023-01-28 14:03:58",-0.804831],
[4,"wave.sin","2023-01-28 14:03:58",0.593504]
]
}
}CSV
Use --format csv option
machbase-neo shell sql \
--format csv \
"select * from EXAMPLE order by time desc limit 4"#,NAME,TIME(UTC),VALUE
1,wave.sin,2023-01-28 14:03:59,0.214839
2,wave.cos,2023-01-28 14:03:59,-0.976649
3,wave.cos,2023-01-28 14:03:58,-0.804831
4,wave.sin,2023-01-28 14:03:58,0.593504Use --no-heading option to exclude the first line header
machbase-neo shell sql \
--format csv \
--no-heading \
"select * from EXAMPLE order by time desc limit 4"1,wave.sin,2023-01-28 14:03:59,0.214839
2,wave.cos,2023-01-28 14:03:59,-0.976649
3,wave.cos,2023-01-28 14:03:58,-0.804831
4,wave.sin,2023-01-28 14:03:58,0.593504Query Time format
Use --timeformat option to specify time output format.
Execute help timeformat to display pre-defined formats and syntax for custom format.
machbase-neo shell help timeformatPre-defined timeformats
| Name | Format |
|---|---|
| Default,- | 2006-01-02 15:04:05.999 |
| ns, us, ms, s | (UNIX epoch in nano-, milli-, micro-, seconds as int64) |
| Numeric | 01/02 03:04:05PM ‘06 -0700 |
| RFC822 | 02 Jan 06 15:04 MST |
| RFC850 | Monday, 02-Jan-06 15:04:05 MST |
| RFC3339 | 2006-01-02T15:04:05Z07:00 |
| Kitchen | 3:04:05PM |
| Stamp | Jan _2 15:04:05 |
| …(there are more)… | Please consult machbase-neo shell help timeformat |
Try --timeformat numeric format.
machbase-neo shell sql \
--timeformat numeric \
"select * from example where name='wave.sin' order by time desc limit 1" # NAME TIME(UTC) VALUE
───────────────────────────────────────────────────
1 wave.sin 01/28 02:03:59PM '23 +0000 0.214839-t is a shorten alias of --timeformat
machbase-neo shell sql \
-t ms \
"select * from example where name='wave.sin' order by time desc limit 1" # NAME TIME(UTC) VALUE
──────────────────────────────────────
1 wave.sin 1674914639000 0.214839Custom time format
It is also possible your own custom format.
machbase-neo shell sql \
--timeformat "2006.01.02 (15:04:05.000)" \
"select * from example where name='wave.sin' order by time desc limit 1" # NAME TIME(UTC) VALUE
────────────────────────────────────────────────────
1 wave.sin "2023.01.28 (14:03:59.000)" 0.214839| Value | Symbol |
|---|---|
| year | 2006 |
| month | 01 |
| day | 02 |
| hour | 03 or 15 |
| minute | 04 |
| second | 05 or with sub-seconds ‘05.999’ or ‘05.000’ |
Combine time format and time zone
machbase-neo shell sql \
--tz Europe/Paris \
--timeformat "2006.01.02 (15:04:05.000)" \
"select * from example where name='wave.sin' order by time desc limit 1" # NAME TIME(EUROPE/PARIS) VALUE
────────────────────────────────────────────────────
1 wave.sin "2023.01.28 (15:03:59.000)" 0.214839s,ms,us and ns formats are represents UNIX epoch time.
If one of these formats are used, --tz option is ignored.
Because epoch time is always in UTC.