Bridge - SQLite
Register a bridge to sqlite3
Register a bridge that connects to the SQLite.
bridge add -t sqlite sqlitedb file:/data/sqlite.db;SQLite supports memory only mode like below.
bridge add -t sqlite mem file::memory:?cache=sharedThe command below is equivalent to the web UI shown in the following image.

Test the bridge’s connectivity
machbase-neo» bridge test mem;
Test bridge mem connectivity... success 11.917µs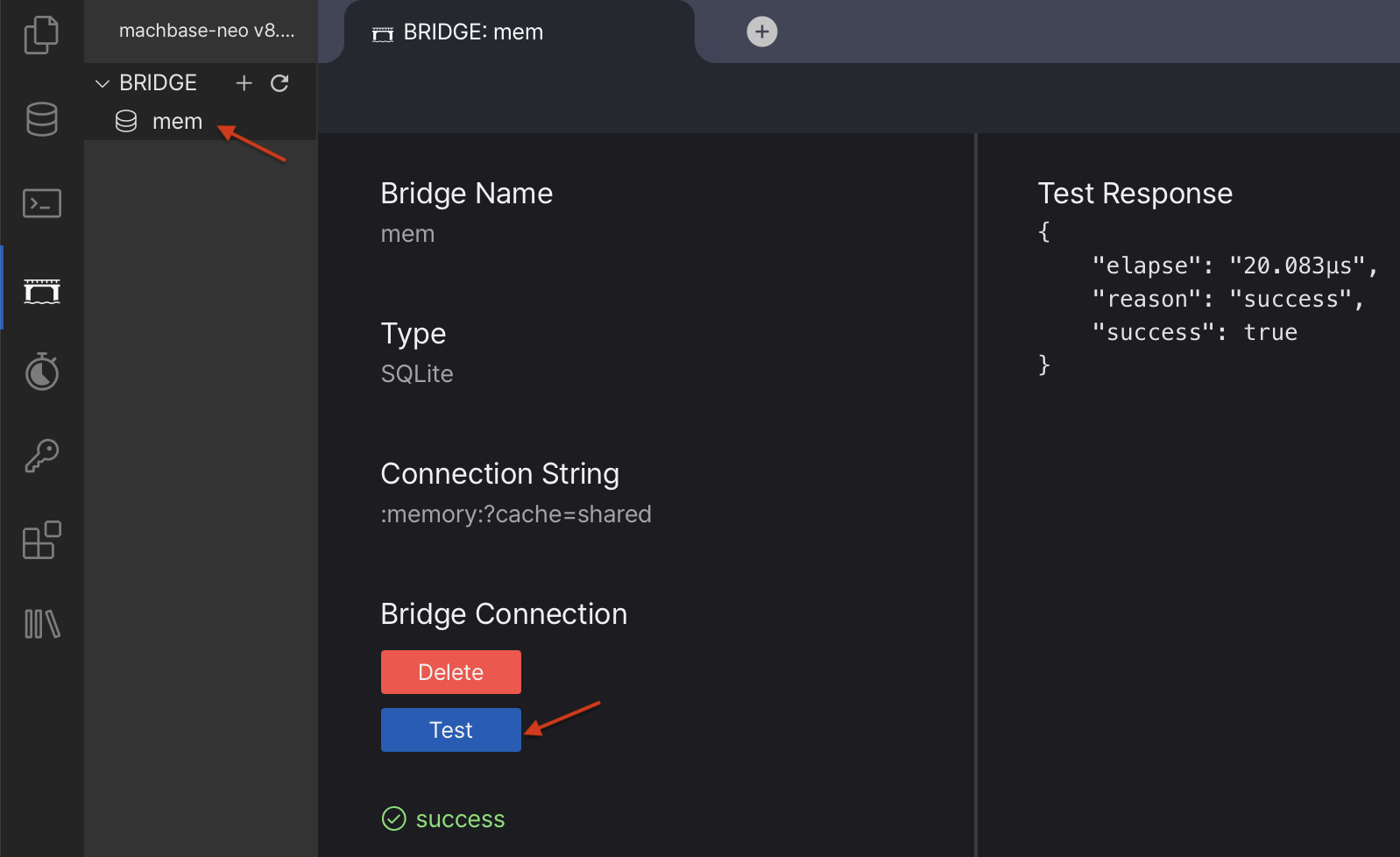
Create table
Open machbase-neo shell and execute the command below which creates a mem_example table via the mem bridge.
bridge exec mem CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS mem_example(
id INTEGER NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
company TEXT,
employee INTEGER,
discount REAL,
code TEXT,
valid BOOLEAN,
memo BLOB,
created_on DATETIME NOT NULL
);The standard SQL editor can execute SQL for the bridged database if there is an -- env: bridge=<name> comment. The env comment remains effective until it is cleared by -- env: reset.
-- env: bridge=mem
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS mem_example(
id INTEGER NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
company TEXT,
employee INTEGER,
discount REAL,
code TEXT,
valid BOOLEAN,
memo BLOB,
created_on DATETIME NOT NULL
);
-- env: reset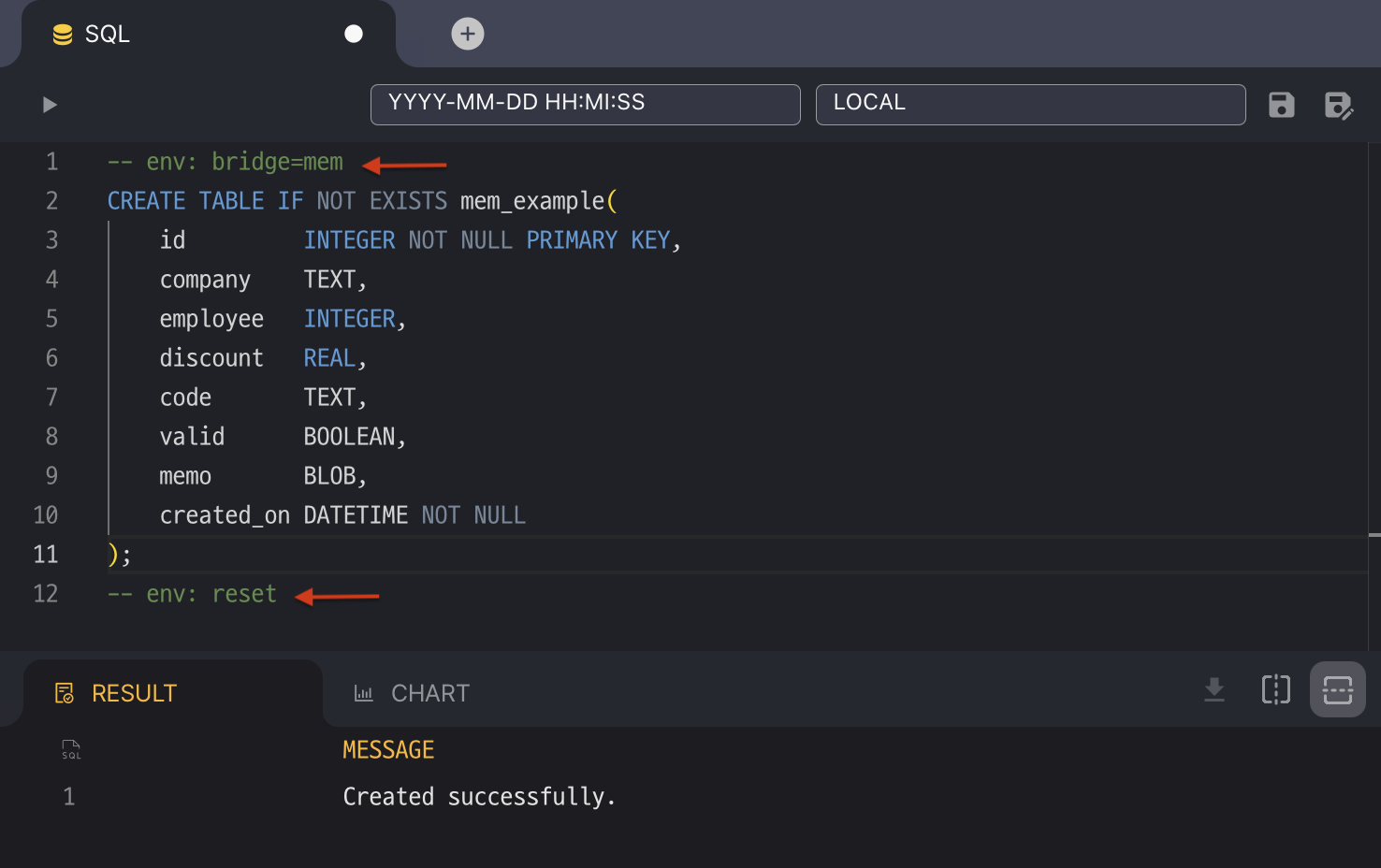
DML on the SQL Editor
-- env: bridge=mem
INSERT INTO mem_example(company, employee, created_on)
values('Fedel-Gaylord', 12, datetime('now'));
INSERT INTO mem_example(company, employee, created_on)
values('Simoni', 23, datetime('now'));
SELECT company, employee, datetime(created_on, 'localtime') from mem_example;
DELETE from mem_example;
-- env: reset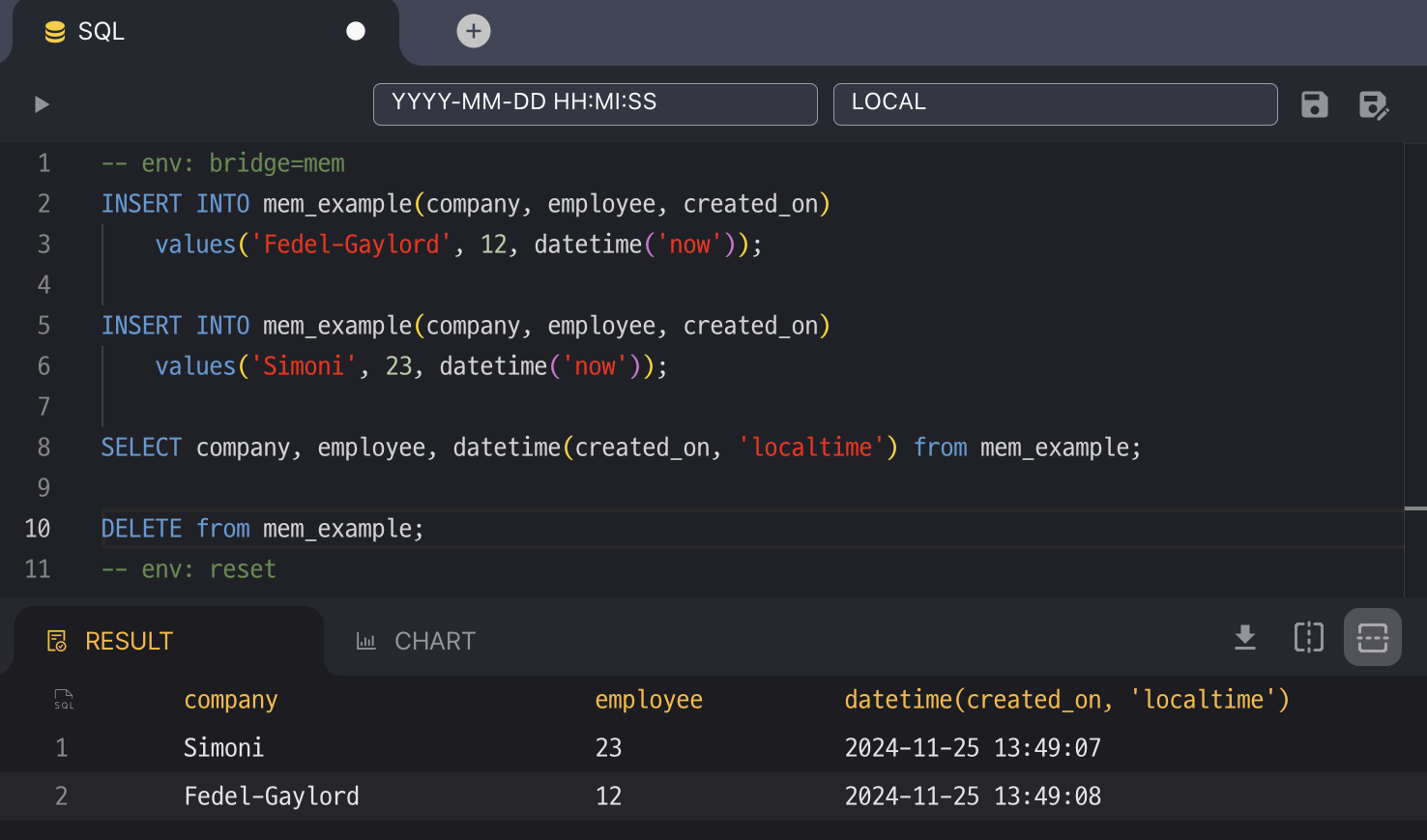
TQL writing on the SQLite
| |
machbase-neo» bridge query mem select * from mem_example;
╭────┬─────────┬──────────┬──────────┬───────┬───────┬──────┬──────────────────────────────────────╮
│ ID │ COMPANY │ EMPLOYEE │ DISCOUNT │ CODE │ VALID │ MEMO │ CREATED_ON │
├────┼─────────┼──────────┼──────────┼───────┼───────┼──────┼──────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 1 │ acme │ 10 │ <nil> │ <nil> │ <nil> │ [] │ 2023-08-10 14:33:08.667491 +0900 KST │
╰────┴─────────┴──────────┴──────────┴───────┴───────┴──────┴──────────────────────────────────────╯TQL reading from the SQLite
Save the code below as sqlite.tql.
SQL(bridge('mem'), "select company, employee, created_on from mem_example")
CSV()And call the endpoint with curl command or open the browser.
curl -o - http://127.0.0.1:5654/db/tql/sqlite.tqlNovaWave,10,1704866777160399000
Sunflower,20,1704866777160407000Copy data from/to SQLite
This example demonstrates how to copy data from Machbase to an SQLite bridge.
Bridge
Define a sqlite bridge with the following details:
- Type:
SQLite - Connection string:
file:///tmp/sqlite.db
SQL
Create the example table in the SQLite database located at “/tmp/sqlite.db”.
--env: bridge=sqlite
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS example (
NAME TEXT,
TIME DATETIME,
VALUE REAL
);
-- env: resetTQL
The TQL script below executes a SELECT statement using the SQL() function to retrieve the required data,
and then writes the data into the SQLite database using the INSERT() function with bridge("sqlite") as the first argument.
SQL(`select name, time, value from example where name = 'my-car'`)
INSERT(bridge("sqlite"), "name", "time", "value", table("example"))SQL
--env: bridge=sqlite
SELECT * FROM example order by TIME;
-- env: reset