Timer
A timer defines a task that should be executed at a given time or repeatedly at a given interval.
Add new timer
Register a task that runs on the specified schedule. The web ui for managing timers has been included Since v8.0.20 .
Select the
 icon from the left side menu bar.
icon from the left side menu bar.Click
+of from the top left.
from the top left.Set timer id (name), timer spec, and task TQL path.
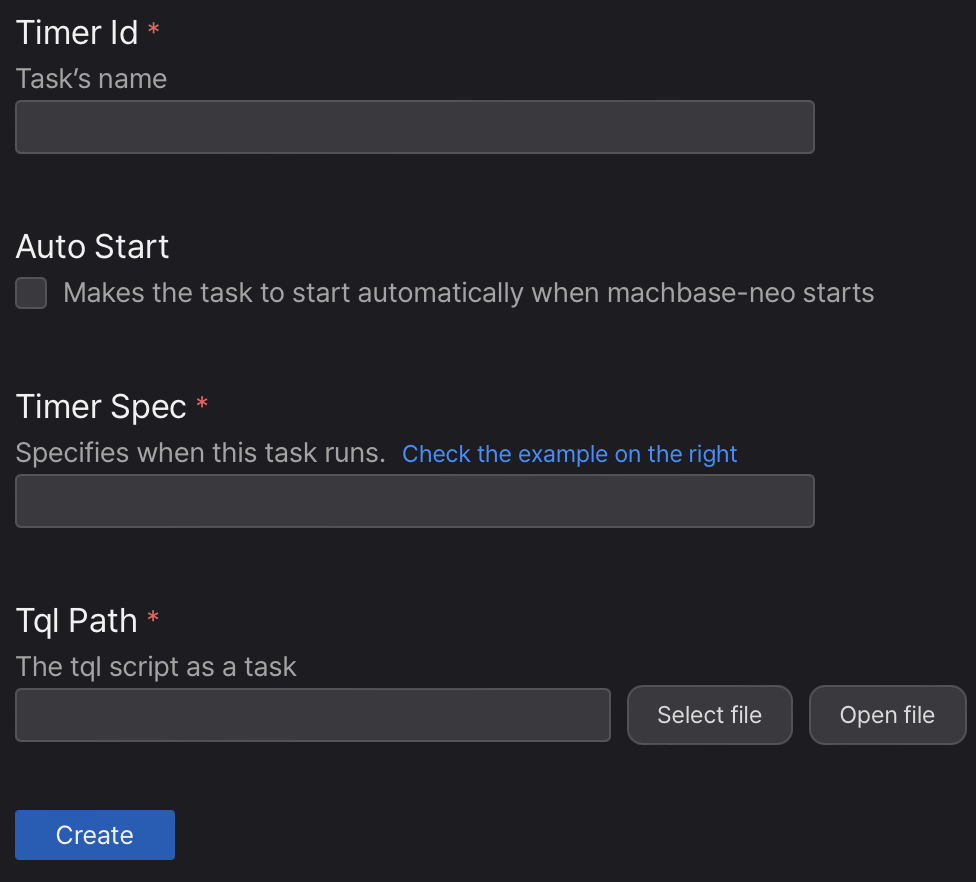
- Click “Create” button.
Start/Stop/Delete timer
Use the toggle button  to start and
to start and  to stop the timer.
to stop the timer.
Timer Schedule Spec.
There three possible examples)
0 30 * * * * Every hour on the half hour
@every 1h30m Every hour thirty
@daily Every dayCRON expression
| Field name | Mandatory? | Allowed values | Allowed special characters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seconds | Yes | 0-59 | * / , - |
| Minutes | Yes | 0-59 | * / , - |
| Hours | Yes | 0-23 | * / , - |
| Day of month | Yes | 1-31 | * / , - ? |
| Month | Yes | 1-12 or JAN-DEC | * / , - |
| Day of week | Yes | 0-6 or SUN-SAT | * / , - ? |
Asterisk
*
The asterisk indicates that the cron expression will match for all values of the field; e.g., using an asterisk in the 5th field (month) would indicate every month.Slash
/
Slashes are used to describe increments of ranges. For example 3-59/15 in the 1st field (minutes) would indicate the 3rd minute of the hour and every 15 minutes thereafter. The form “*/…” is equivalent to the form “first-last/…”, that is, an increment over the largest possible range of the field. The form “N/…” is accepted as meaning “N-MAX/…”, that is, starting at N, use the increment until the end of that specific range. It does not wrap around.Comma
,
Commas are used to separate items of a list. For example, using “MON,WED,FRI” in the 5th field (day of week) would mean Mondays, Wednesdays and Fridays.Hyphen
-
Hyphens are used to define ranges. For example, 9-17 would indicate every hour between 9am and 5pm inclusive.Question mark
?
Question mark may be used instead of*for leaving either day-of-month or day-of-week blank.
Predefined schedules
| Entry | Description | Equivalent To |
|---|---|---|
| @yearly (or @annually) | Run once a year, midnight, Jan. 1st | 0 0 0 1 1 * |
| @monthly | Run once a month, midnight, first of month | 0 0 0 1 * * |
| @weekly | Run once a week, midnight between Sat/Sun | 0 0 0 * * 0 |
| @daily (or @midnight) | Run once a day, midnight | 0 0 0 * * * |
| @hourly | Run once an hour, beginning of hour | 0 0 * * * * |
Intervals
@every <duration> where “duration” is a string that is a possibly signed sequence of decimal numbers,
each with optional fraction and a unit suffix, such as “300ms”, “-1.5h” or “2h45m”. Valid time units are “ms”, “s”, “m”, “h”.
@every 10h
@every 1h10m30sCommand line
Add timer
Syntax: timer add [--autostart] <name> <timer_spec> <tql-path>
--autostartmakes the task will start automatically when machbase-neo starts. If the task is not autostart mode, you can make it start and stop manually bytimer start <name>andtimer stop <name>commands.<name>task’s name<timer_spec>specifies when this task runs. (see below)<tql-path>the tql script as a task
List timers
Syntax: timer list
Start/Stop timer
Syntax: timer [start | stop] <name>
Delete timer
Syntax: timer del <name>
Hello World? Example
Let’s make the “Hello World” of the timer.
Make a tql of “Hello World”
Open tql editor, copy the code below and save it as helloworld.tql.
CSV(`helloworld,0,0`)
MAPVALUE(1, time('now'))
MAPVALUE(2, random())
INSERT("name", "time", "value", table("example"))Execute the script and it inserts a single record into the EXAMPLE table. Run SELECT SQL to see if it works correctly.
select * from example where name = 'helloworld';sys machbase-neo» select * from example where name = 'helloworld';
┌────────┬────────────┬─────────────────────────┬────────────────────┐
│ ROWNUM │ NAME │ TIME(LOCAL) │ VALUE │
├────────┼────────────┼─────────────────────────┼────────────────────┤
│ 1 │ helloworld │ 2024-06-19 18:20:07.001 │ 0.6132387755535856 │
└────────┴────────────┴─────────────────────────┴────────────────────┘
a row fetched.Register a timer
This timer function on the web, introduced in version 8.0.20, can be achieved using the following shell commands.
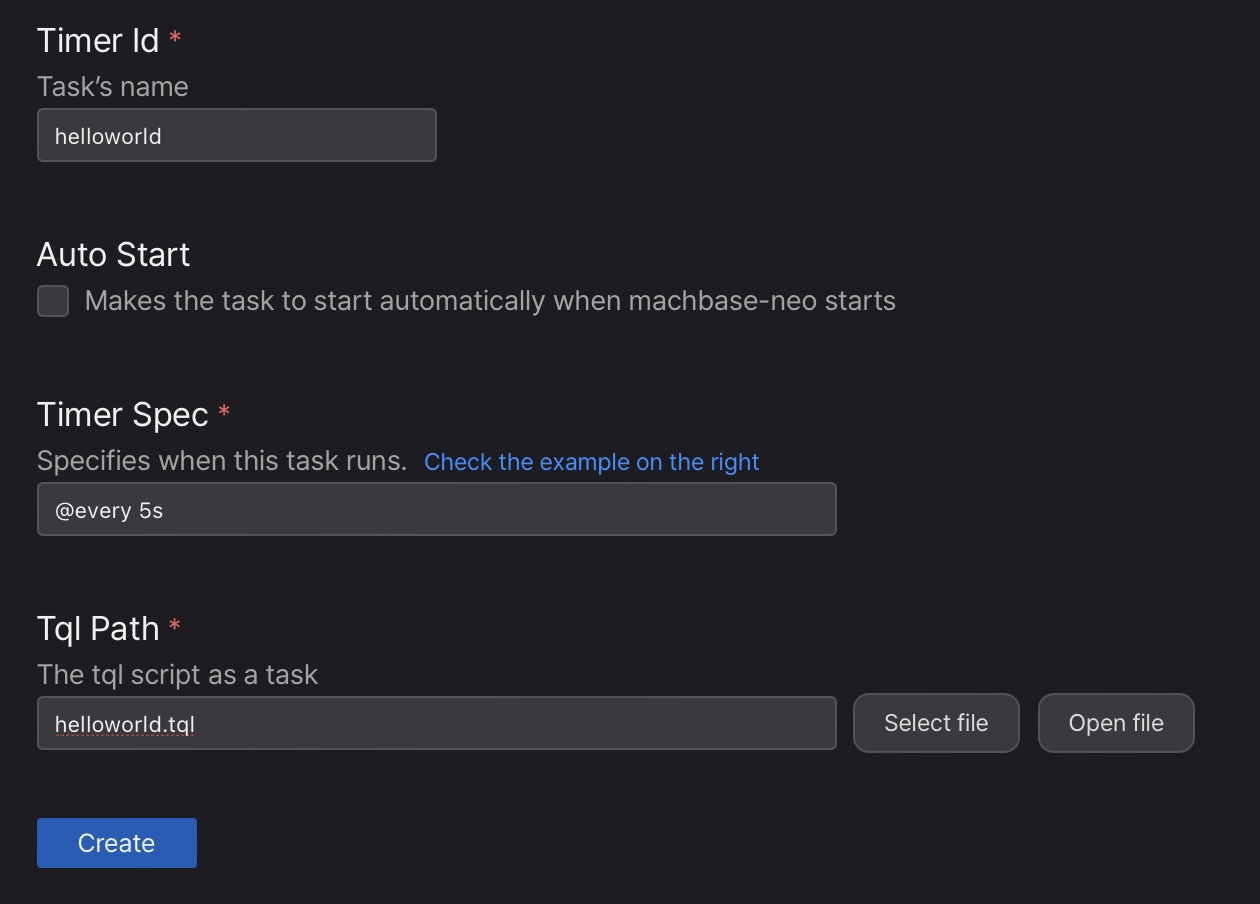
This is equivalent with the command line below.
timer add helloworld "@every 5s" helloworld.tql; Make the new timer to be started by check “Auto Start” option or do it manually by toggle  button.
button.
As soon as it starts, the new record will be inserted into the table at every 5 seconds.
Query the result of the timer
sys machbase-neo» select * from example where name = 'helloworld';
┌────────┬────────────┬─────────────────────────┬─────────────────────┐
│ ROWNUM │ NAME │ TIME(LOCAL) │ VALUE │
├────────┼────────────┼─────────────────────────┼─────────────────────┤
│ 1 │ helloworld │ 2024-07-03 09:49:47.002 │ 0.14047743934840562 │
│ 2 │ helloworld │ 2024-07-03 09:49:42.002 │ 0.7656153597963373 │
│ 3 │ helloworld │ 2024-07-03 09:49:37.002 │ 0.11713331640146182 │
│ 4 │ helloworld │ 2024-07-03 09:49:32.002 │ 0.5351642943247759 │
│ 5 │ helloworld │ 2024-07-03 09:49:27.001 │ 0.6588127185612987 │
└────────┴────────────┴─────────────────────────┴─────────────────────┘
5 rows fetched.Dashboard
Create a dashboard to refresh automatically and watch the timer works as expected.
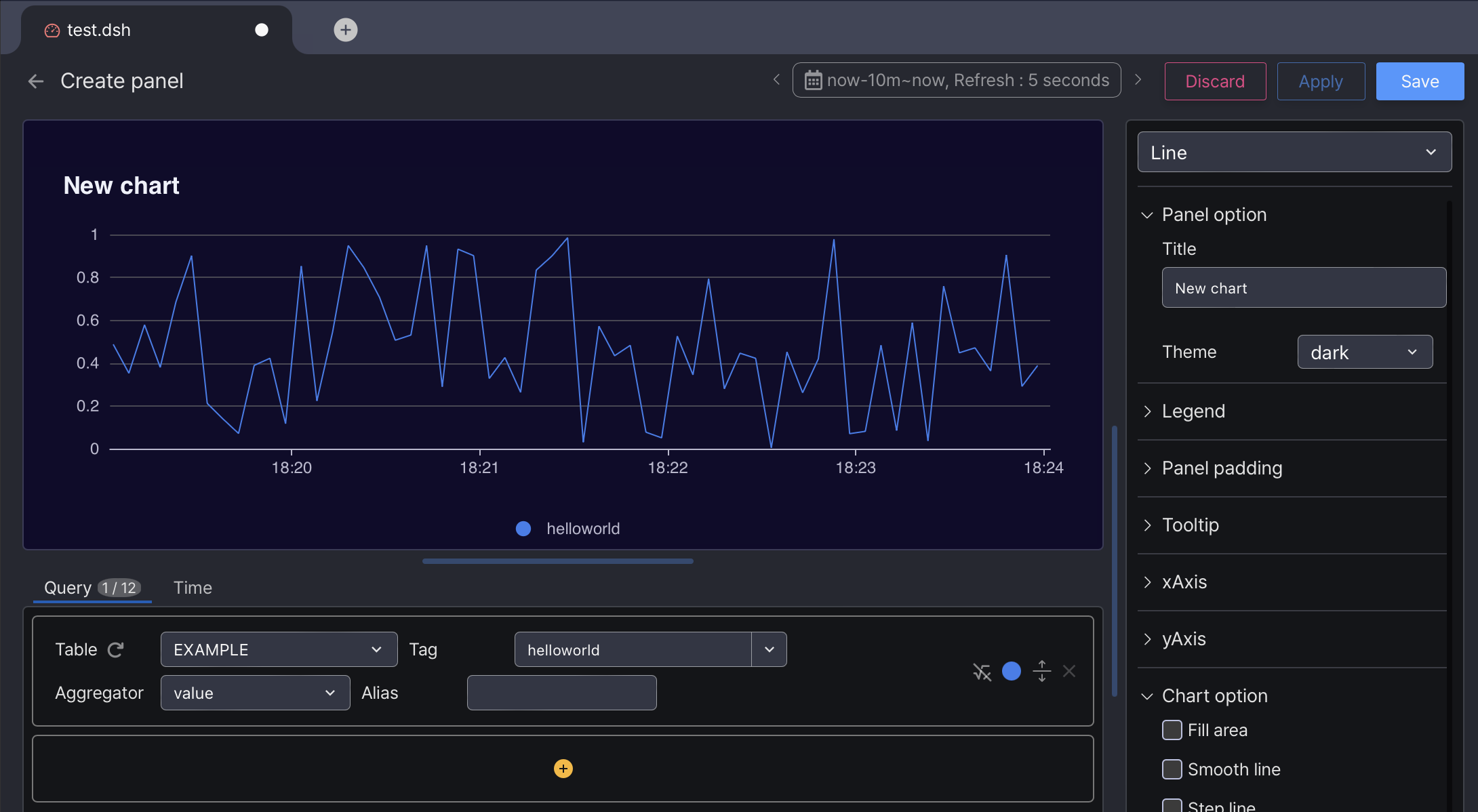
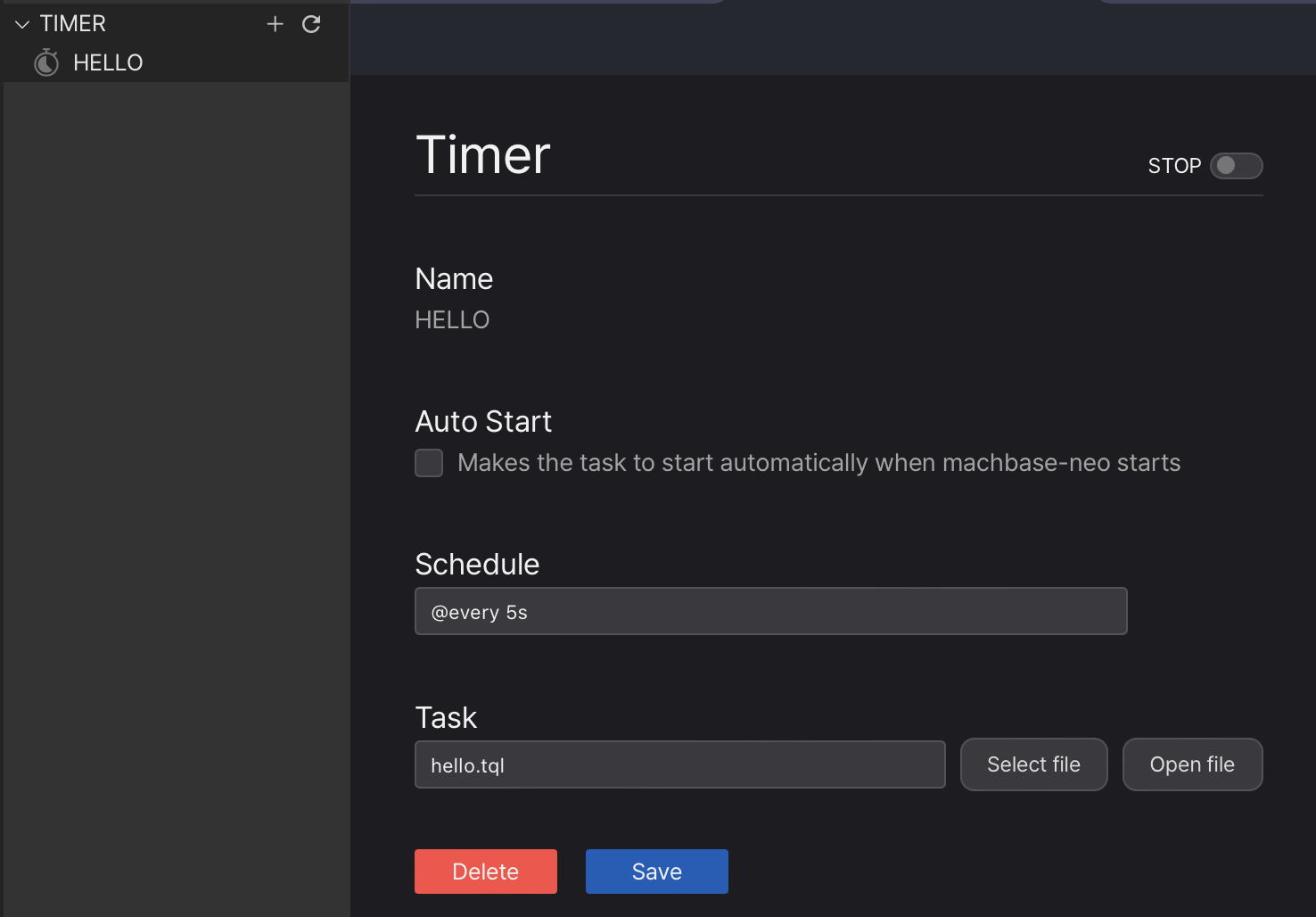
Manage timers
It is possible edit, start, stop and delete from the detail page.
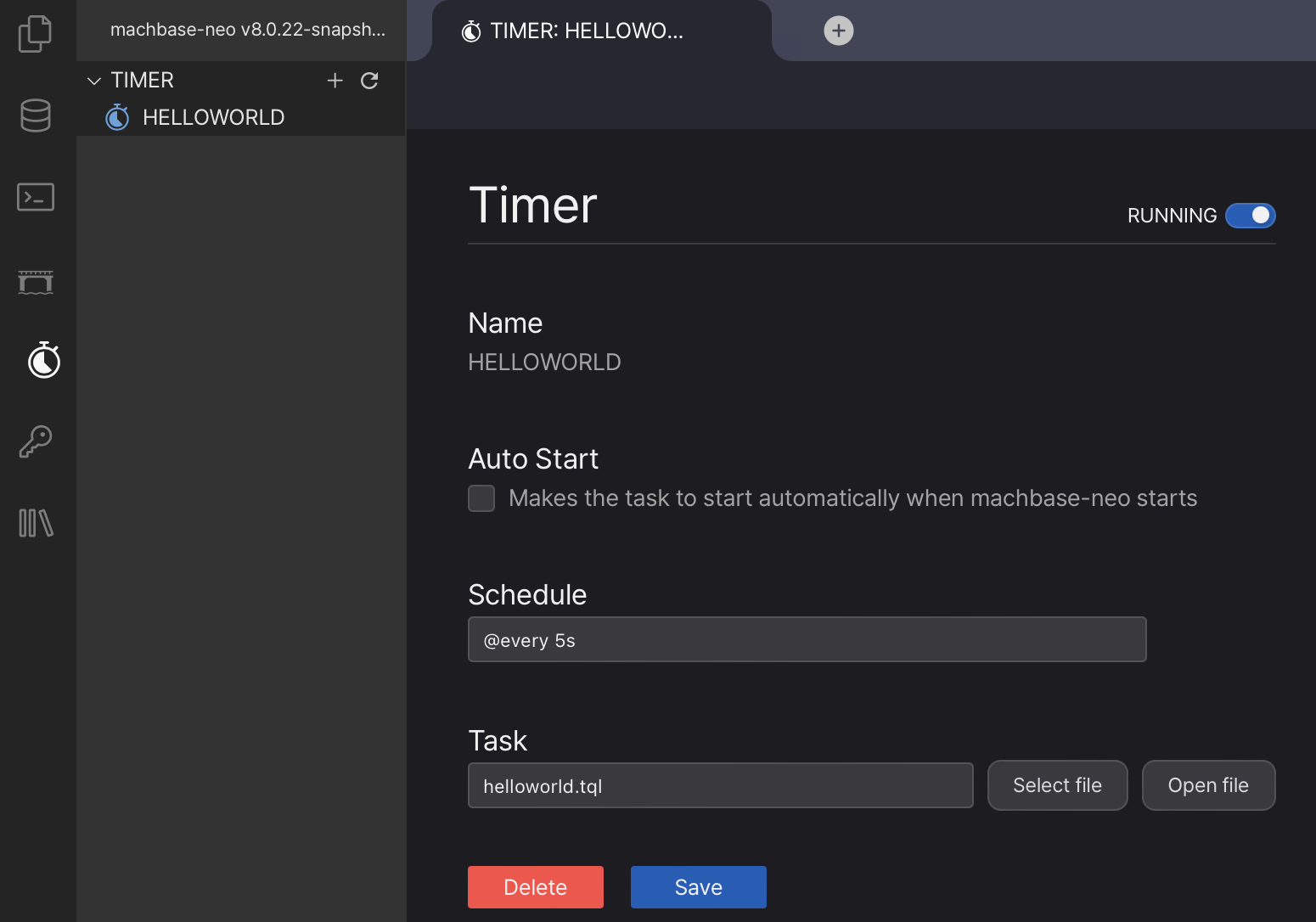
Command line
The command timer list shows the status of timers.
sys machbase-neo» timer list;
┌────────────┬───────────┬────────────────┬───────────┬─────────┐
│ NAME │ SPEC │ TQL │ AUTOSTART │ STATE │
├────────────┼───────────┼────────────────┼───────────┼─────────┤
│ HELLOWORLD │ @every 5s │ helloworld.tql │ false │ RUNNING │
└────────────┴───────────┴────────────────┴───────────┴─────────┘Also it is possible to start, stop the timer from the command line.
timer start helloworld;timer stop helloworld;