Let's make waves
This tutorial shows how to write and read database only with shell scripts.
CREATE TAG TABLE IF NOT EXISTS EXAMPLE (
NAME VARCHAR(20) PRIMARY KEY,
TIME DATETIME BASETIME,
VALUE DOUBLE SUMMARIZED
);Write data
The simplest way writing data into machbase-neo is using its command line tool machbase-neo shell.
We can import/export/read table with it.
Data generation
For demonstration, we prepares simple shell script that prints out sine/cosine values per a second.
Copy script below and save it as gen_wave.sh
#!/bin/bash
angle=0
step_angle=24
sinval=0
cosval=0
PI=3.14159
while [ 1 ]
do
ts=`date +"%s"`
sinval=$(awk "BEGIN{ printf \"%.6f\", (sin($angle*($PI/180)))}")
cosval=$(awk "BEGIN{ printf \"%.6f\", (cos($angle*($PI/180)))}")
echo "wave.sin,$ts,$sinval"
echo "wave.cos,$ts,$cosval"
sleep 1
angle=$((angle+step_angle))
doneRun script
Let’s run this script for testing.
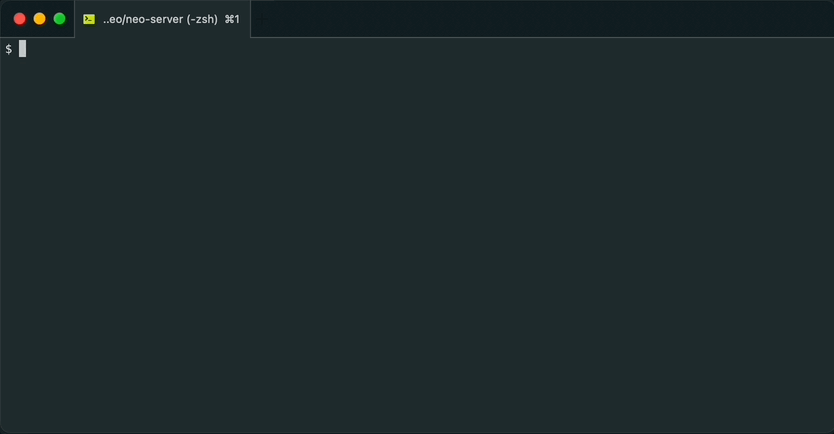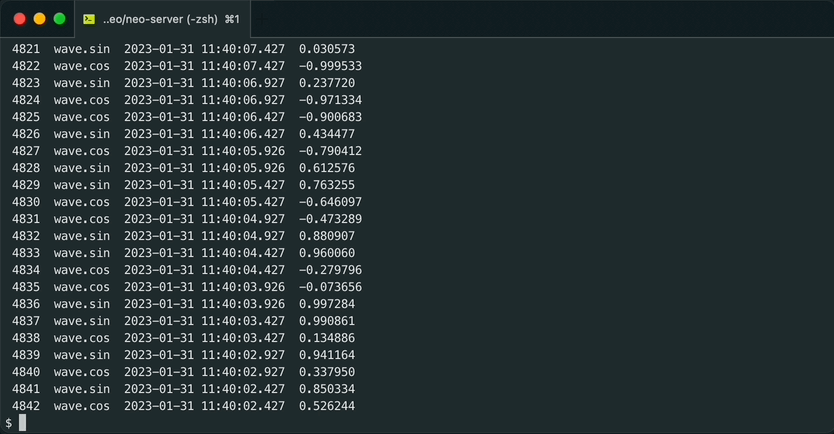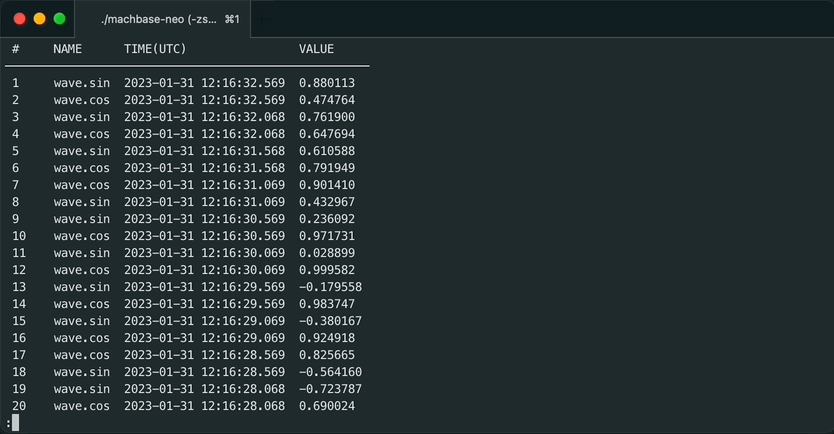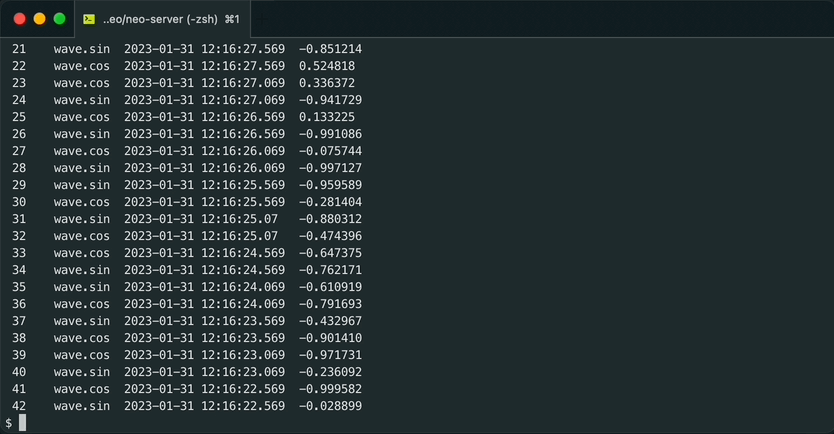
sh ./gen_wave.shIt periodically prints sin/cos values with name (wave.sin, wave.cos), UNIX epoch time and value per a second as below.
The output is in csv and it is intended to be utilized by machbase-neo shell command.
Press ^C to stop shell script.

Why the output csv should be in this order? It’s depends on the table scheme.
Run command below to “describe” the table.
machbase-neo shell desc EXAMPLESubcommand desc <table> shows some details of the table.
TABLE EXAMPLE
TYPE Tag Table
TAGS wave.cos, wave.sin
┌───┬───────┬──────────┬────────┐
│ # │ NAME │ TYPE │ LENGTH │
├───┼───────┼──────────┼────────┤
│ 1 │ NAME │ varchar │ 100 │
│ 2 │ TIME │ datetime │ 8 │
│ 3 │ VALUE │ double │ 8 │
└───┴───────┴──────────┴────────┘When we import the csv data into a table, it is important to make fields of csv arranged in order of columns in the table and its type.
Combine script and command
Now we can use the output of the script for input of machbase-neo shell.
sh gen_wave.sh | machbase-neo shell import --timeformat=s EXAMPLESince machbase-neo treats all timestamp in nanoseconds, but shell script generates timestamp in seconds by
time shell command.
It is required explicitly announce to machbase-neo
that incoming timestamp of csv data
is in seconds time precision by --timeformat.Consult
machbase-neo shell help timeformat for more details.A each line of CSV that are generated by shell script is processed in machbase-neo shell import then “import” into EXAMPLE table.
This means also we can write data manually as an example below.
echo "wave.pi,1674860125,3.141592" | machbase-neo shell import -t s EXAMPLEor
echo "wave.pi,`date +%s`,3.141592" | machbase-neo shell import -t s EXAMPLEThen let’s query the latest value.
machbase-neo shell "select * from EXAMPLE where NAME='wave.pi' order by time desc limit 1"
Read data
SQL Query
While writing script is running…
sh gen_wave.sh | machbase-neo shell import --timeformat=s EXAMPLEPrint out data by using “SQL query”.
machbase-neo shell "select * from EXAMPLE order by time desc" # NAME TIME(UTC) VALUE
────────────────────────────────────────────────
1 wave.sin 2023-01-28 14:03:59 0.214839
2 wave.cos 2023-01-28 14:03:59 -0.976649
3 wave.sin 2023-01-28 14:03:58 0.593504
4 wave.cos 2023-01-28 14:03:58 -0.804831
...
We executed query by machbase-neo shell without sql sub-command above example.
It properly printed out result of query which is because machbase-neo shell takes sql sub-command as default as long as there are no other arguments and flags. This means machbase-neo shell "select..." is same with machbase-neo shell sql "select...".
So when we use some flags for executing query, explicitly specify sql subcommand like below.
machbase-neo shell sql \
--tz America/Los_Angeles \
"select * from EXAMPLE order by time desc limit 4" # NAME TIME(AMERICA/LOS_ANGELES) VALUE
───────────────────────────────────────────────────
1 wave.sin 2023-01-28 06:03:59 0.214839
2 wave.cos 2023-01-28 06:03:59 -0.976649
3 wave.cos 2023-01-28 06:03:58 -0.804831
4 wave.sin 2023-01-28 06:03:58 0.593504Machbase treats all time data in UTC as default.
Use --tz option to display time in any time-zone other than ‘UTC’ like above example.
This flag accepts ’local’ and tz database format (eg: ‘Europe/Paris’).
machbase-neo shell sql \
--tz local \
"select * from EXAMPLE order by time desc limit 4" # NAME TIME(LOCAL) VALUE
─────────────────────────────────────────────
1 wave.sin 2023-01-28 23:03:59 0.214839
2 wave.cos 2023-01-28 23:03:59 -0.976649
3 wave.cos 2023-01-28 23:03:58 -0.804831
4 wave.sin 2023-01-28 23:03:58 0.593504Table view
It is also possible browsing query result forward/backward with “walk” command like below.
machbase-neo shell walk "select * from EXAMPLE order by time desc"Then you can scroll up/down with keyboard, press ESC to exit table view.
Press r to re-execute query to refresh result, it is particularly useful with query was sorted by order by time desc to see the latest values when data is continuously being written.
Query Output format
JSON
Use --format json option
machbase-neo shell sql \
--format json \
"select * from EXAMPLE order by time desc limit 4"{
"data": {
"columns": ["ROWNUM","NAME","TIME(UTC)","VALUE"],
"types": ["string","string","datetime","double"],
"rows": [
[1,"wave.sin","2023-01-28 14:03:59",0.214839],
[2,"wave.cos","2023-01-28 14:03:59",-0.976649],
[3,"wave.cos","2023-01-28 14:03:58",-0.804831],
[4,"wave.sin","2023-01-28 14:03:58",0.593504]
]
}
}CSV
Use --format csv option
machbase-neo shell sql \
--format csv \
"select * from EXAMPLE order by time desc limit 4"#,NAME,TIME(UTC),VALUE
1,wave.sin,2023-01-28 14:03:59,0.214839
2,wave.cos,2023-01-28 14:03:59,-0.976649
3,wave.cos,2023-01-28 14:03:58,-0.804831
4,wave.sin,2023-01-28 14:03:58,0.593504Use --no-heading option to exclude the first line header
machbase-neo shell sql \
--format csv \
--no-heading \
"select * from EXAMPLE order by time desc limit 4"1,wave.sin,2023-01-28 14:03:59,0.214839
2,wave.cos,2023-01-28 14:03:59,-0.976649
3,wave.cos,2023-01-28 14:03:58,-0.804831
4,wave.sin,2023-01-28 14:03:58,0.593504Query Time format
Use --timeformat option to specify time output format.
Execute help timeformat to display pre-defined formats and syntax for custom format.
machbase-neo shell help timeformatPre-defined timeformats
| Name | Format |
|---|---|
| Default,- | 2006-01-02 15:04:05.999 |
| ns, us, ms, s | (UNIX epoch in nano-, milli-, micro-, seconds as int64) |
| Numeric | 01/02 03:04:05PM ‘06 -0700 |
| RFC822 | 02 Jan 06 15:04 MST |
| RFC850 | Monday, 02-Jan-06 15:04:05 MST |
| RFC3339 | 2006-01-02T15:04:05Z07:00 |
| Kitchen | 3:04:05PM |
| Stamp | Jan _2 15:04:05 |
| …(there are more)… | Please consult machbase-neo shell help timeformat |
Try --timeformat numeric format.
machbase-neo shell sql \
--timeformat numeric \
"select * from example where name='wave.sin' order by time desc limit 1" # NAME TIME(UTC) VALUE
───────────────────────────────────────────────────
1 wave.sin 01/28 02:03:59PM '23 +0000 0.214839-t is a shorten alias of --timeformat
machbase-neo shell sql \
-t ms \
"select * from example where name='wave.sin' order by time desc limit 1" # NAME TIME(UTC) VALUE
──────────────────────────────────────
1 wave.sin 1674914639000 0.214839Custom time format
It is also possible your own custom format.
machbase-neo shell sql \
--timeformat "2006.01.02 (15:04:05.000)" \
"select * from example where name='wave.sin' order by time desc limit 1" # NAME TIME(UTC) VALUE
────────────────────────────────────────────────────
1 wave.sin "2023.01.28 (14:03:59.000)" 0.214839| Value | Symbol |
|---|---|
| year | 2006 |
| month | 01 |
| day | 02 |
| hour | 03 or 15 |
| minute | 04 |
| second | 05 or with sub-seconds ‘05.999’ or ‘05.000’ |
Combine time format and time zone
machbase-neo shell sql \
--tz Europe/Paris \
--timeformat "2006.01.02 (15:04:05.000)" \
"select * from example where name='wave.sin' order by time desc limit 1" # NAME TIME(EUROPE/PARIS) VALUE
────────────────────────────────────────────────────
1 wave.sin "2023.01.28 (15:03:59.000)" 0.214839s,ms,us and ns formats are represents UNIX epoch time.
If one of these formats are used, --tz option is ignored.
Because epoch time is always in UTC.